Aviation History: The airplane that never was
First nuclear-powered aircraft didn’t happen

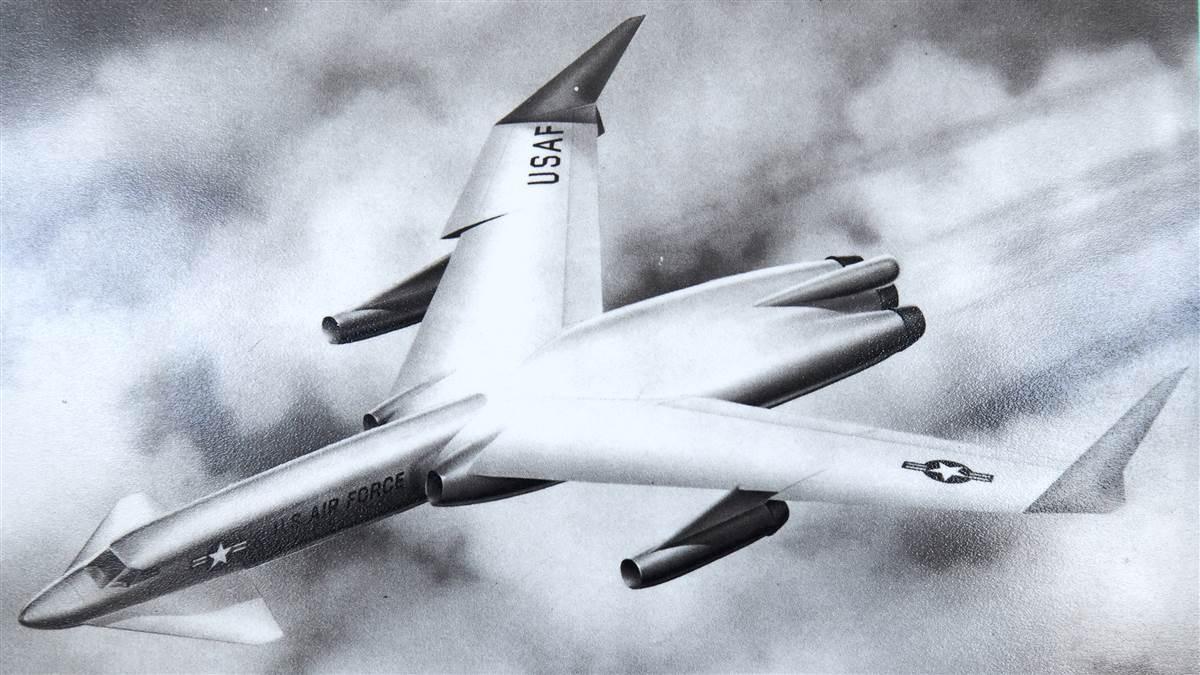
In 1946, after the power of nuclear energy was demonstrated with the bombing of Japan, the U.S. Department of Defense set out to develop a nuclear-powered jet aircraft. The project began with a Convair B–36 bomber as a shield test aircraft. Although one model was modified in the early stages of the project—and prototype engines were developed and flew an on-board operating reactor—the program was canceled before the nuclear-powered aircraft was completed. Because the aircraft’s range would not have been limited by needing to refuel, it was theorized that nuclear-powered aircraft would be able to stay in the air for weeks at a time.
The manned aircraft nuclear propulsion program ran from 1946 until 1961, when—after much back and forth between the Department of Defense, the Air Force, Navy, and the Atomic Energy Commission—President John F. Kennedy stated: “Nearly 15 years and about $1 billion have been devoted to the attempted development of a nuclear-powered aircraft; but the possibility of a militarily useful aircraft in the foreseeable future is still very remote.”
The airplane would have been powered by modified General Electric jet engines. Instead of burning jet fuel, the nuclear jet engine would use the reactor core as a heat source for the turbine’s airflow. Because airflow through the engine was used to cool the reactor, this airflow had to be maintained, even when the aircraft was parked. GE built two prototype engines, and the reactor can be seen outside the Experimental Breeder Reactor I near Arco, Idaho (shown on top).
A 350-foot-wide hangar was built to house the X–6 project, but the project was canceled before the planned 15,000-foot runway was built to accommodate the aircraft’s expected weight.
Other big ideas
Have you heard of these aircraft?
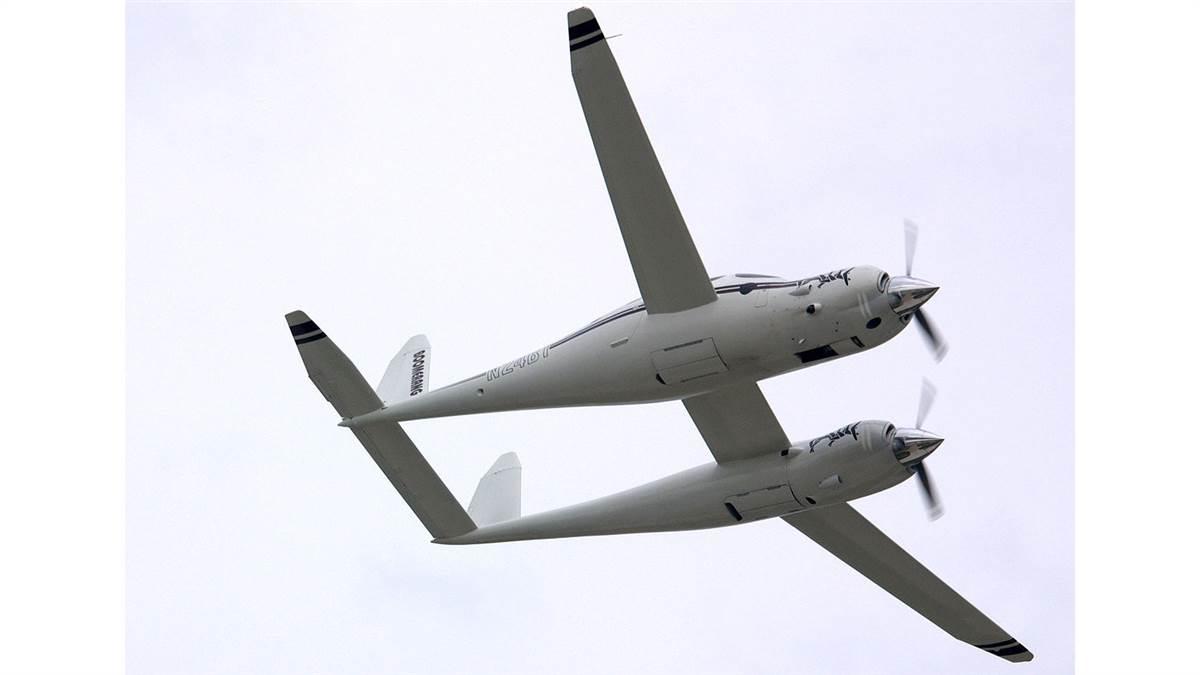

Rutan Boomerang
Burt Rutan’s asymmetric aircraft, introduced in 1996.

Wainfan Facetmobile
A general aviation aircraft that looks like a stealth fighter.
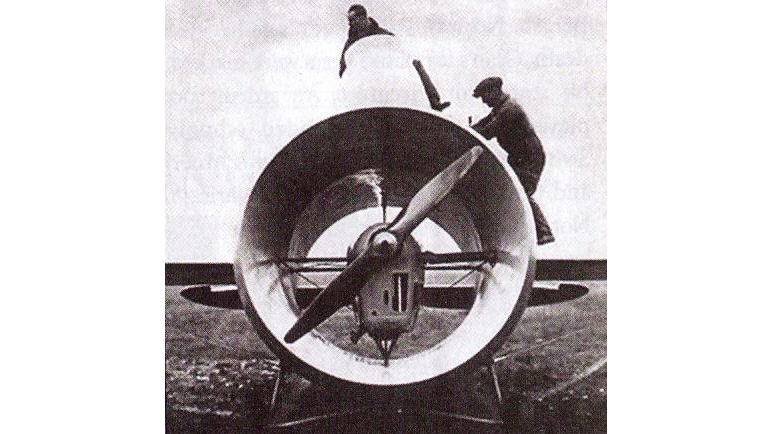
Stipa-Caproni
Known as the “Flying Barrel,” this airplane, whose fuselage was a ducted fan, was developed in Italy in 1932.
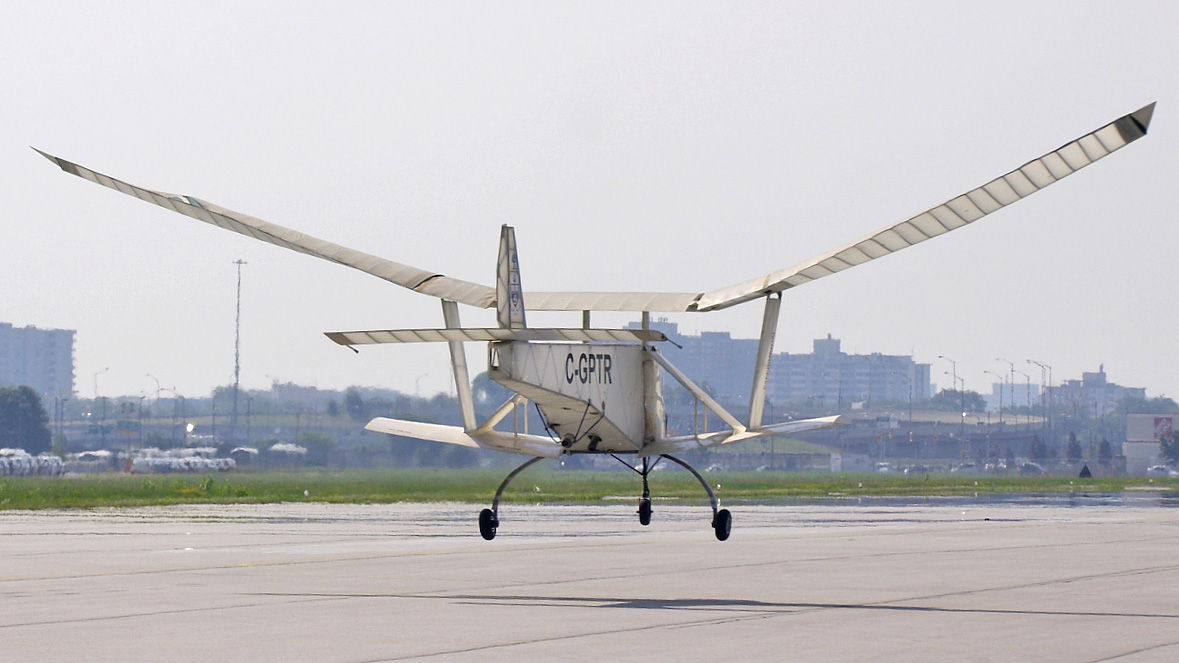

UTIAS Ornithopter
An aircraft that flies by flapping its wings was developed in the late 1990s.

Lun-class Ekranoplan
Soviet battle missile carrier ground-effect vehicle developed in 1987 (NATO named Duck).
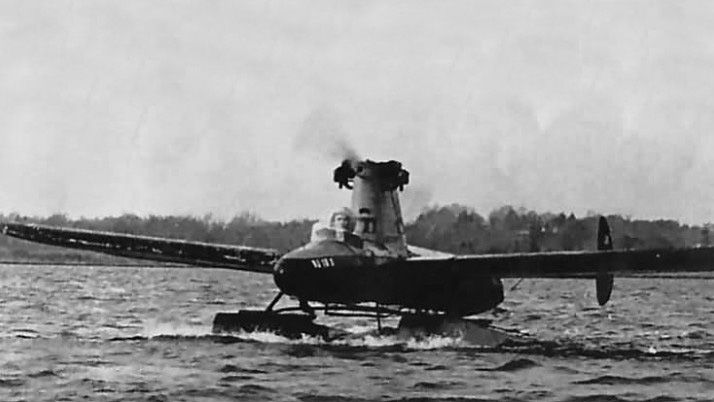

Reid Flying Submarine
Combination seaplane and submarine developed in 1962.
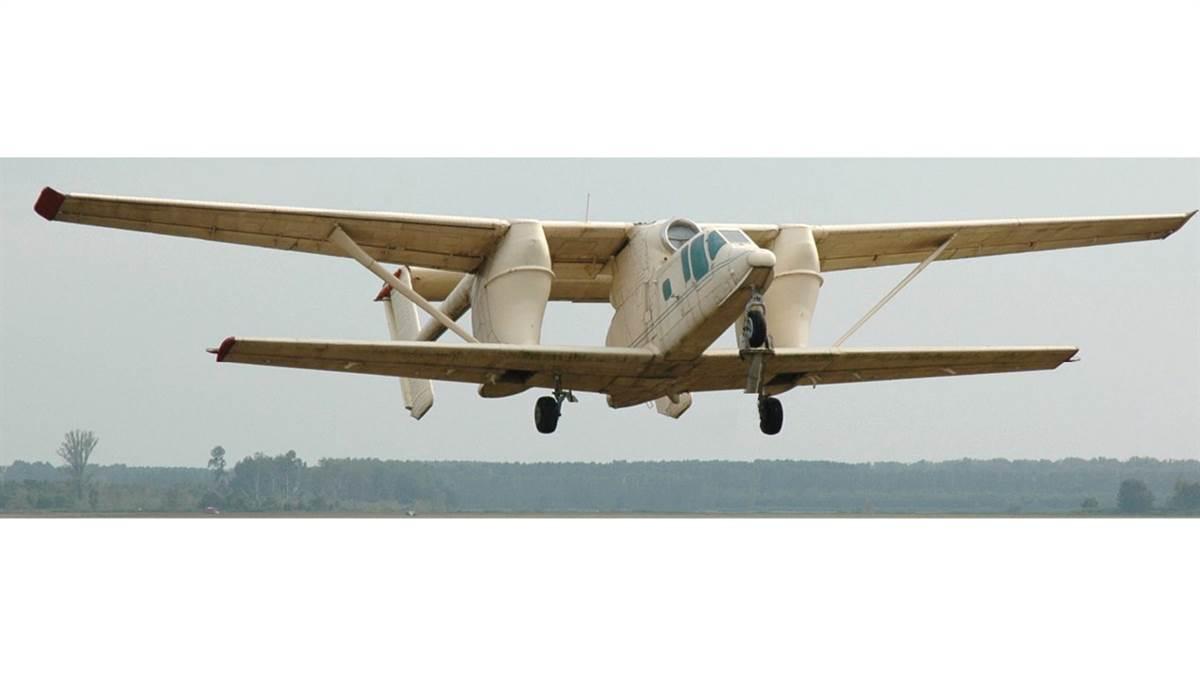

M–15 Belphegor
A Polish design, this jet aircraft was developed in the 1970s for Soviet agriculture use; it is named after the noisy demon Belphegor.
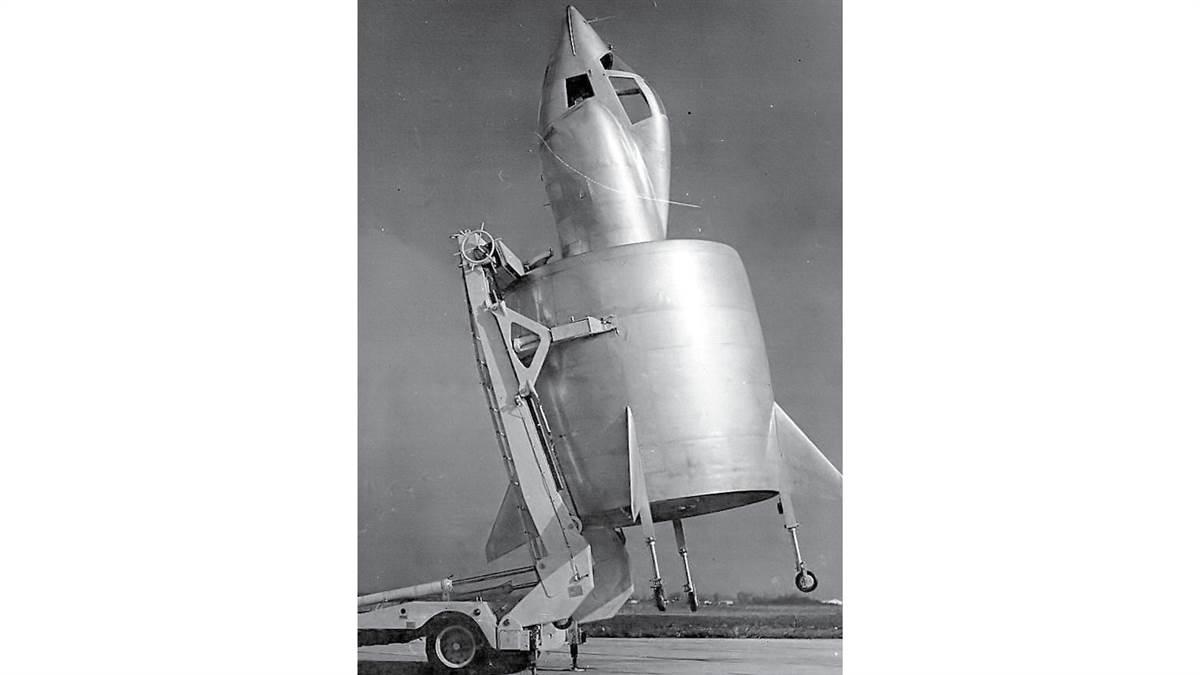

Snecma Coléoptère
French-designed single-person aircraft developed in 1958 to take off and land vertically; coléoptère means “beetle.”
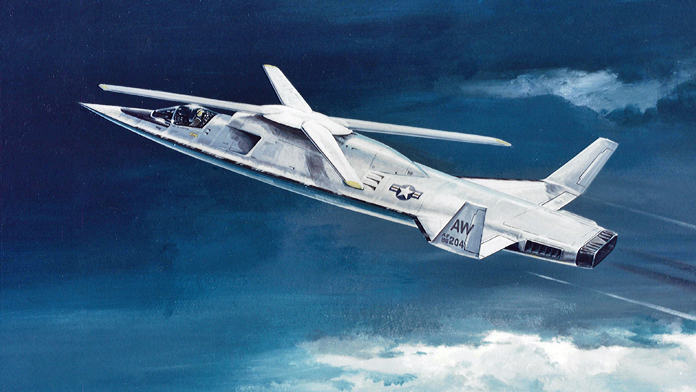
Sikorsky X-Wing
A hybrid helicopter/fixed-wing aircraft that flew in 1976.
 Powerplant
Powerplant 

